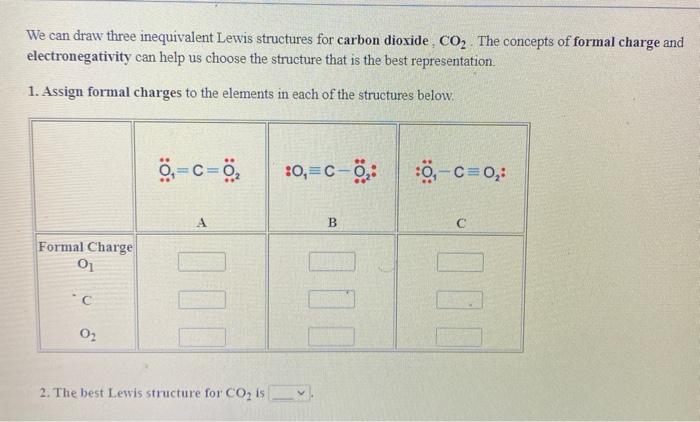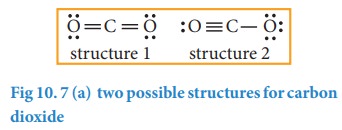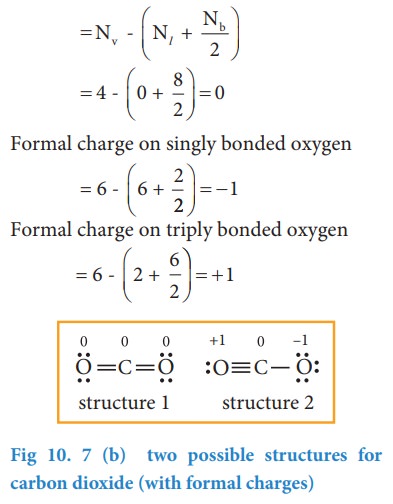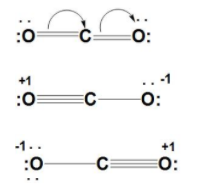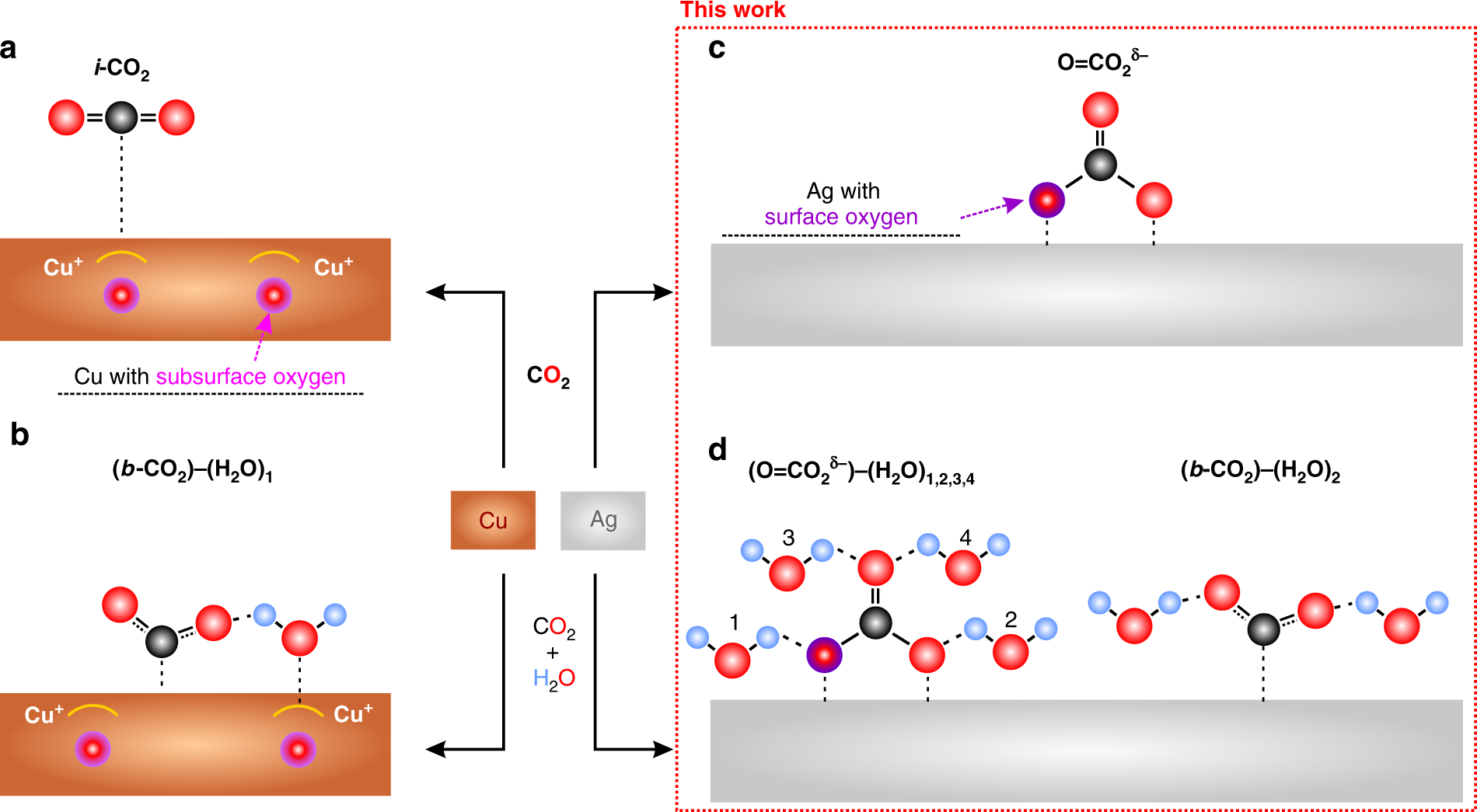
Dramatic differences in carbon dioxide adsorption and initial steps of reduction between silver and copper | Nature Communications
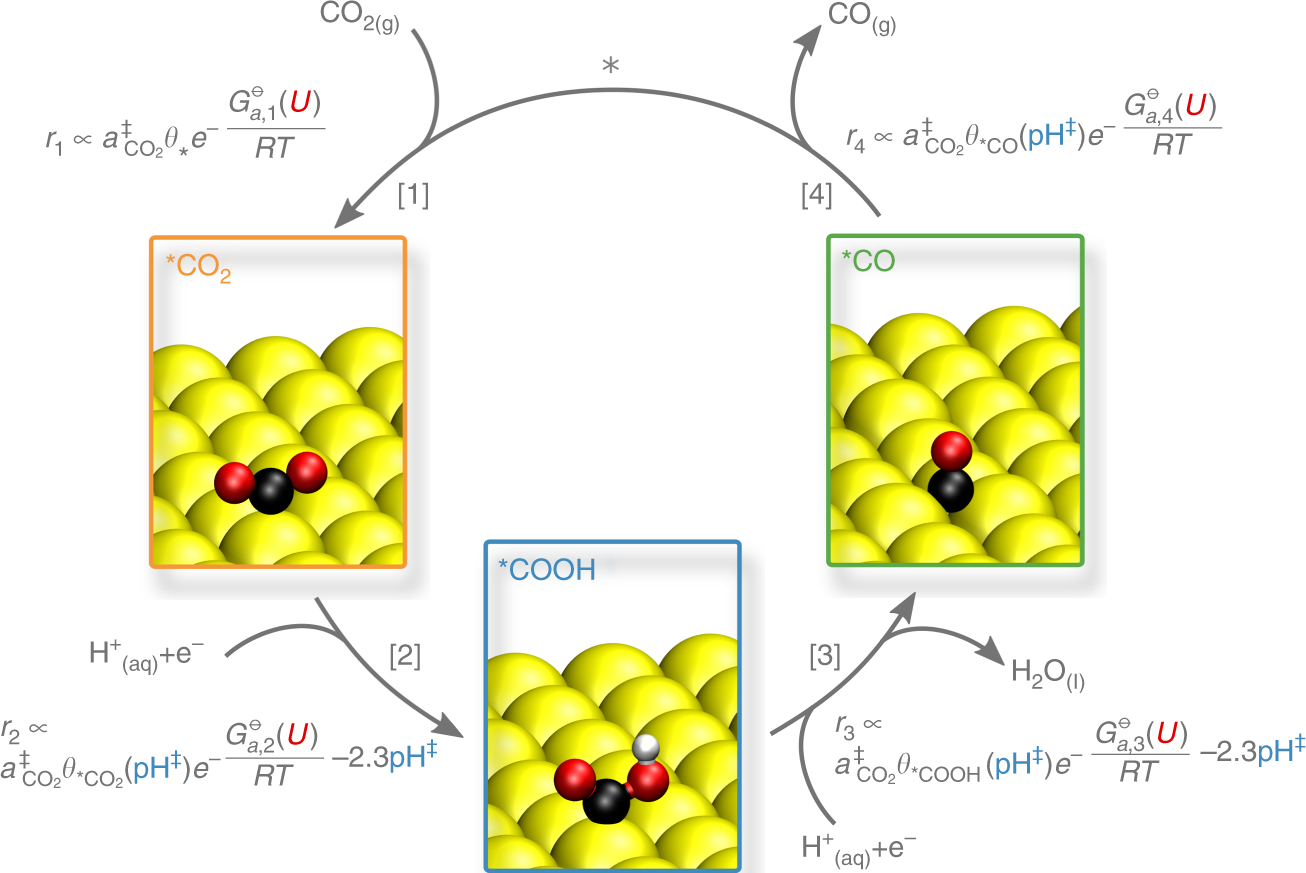
Double layer charging driven carbon dioxide adsorption limits the rate of electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction on Gold | Nature Communications
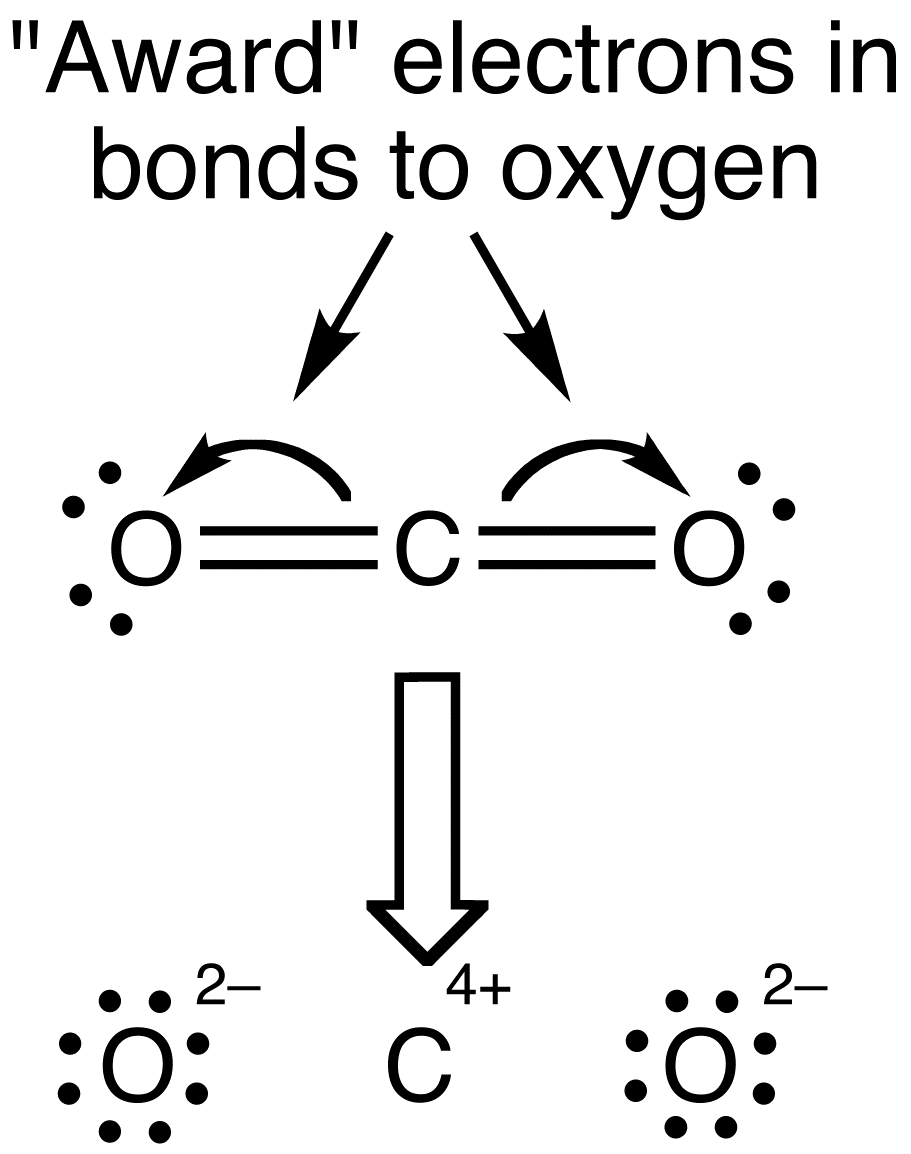
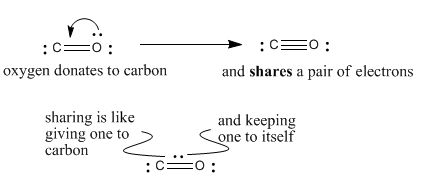
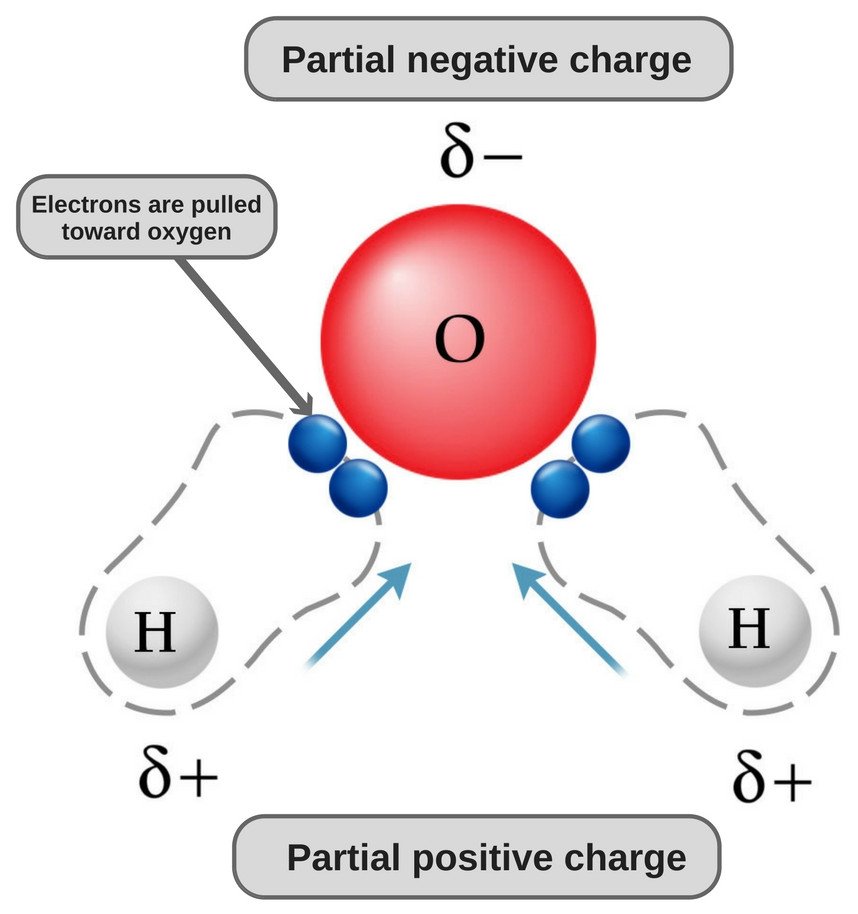
Why does carbon have a small negative charge and oxygen a small positive charge in carbon monoxide? - Quora
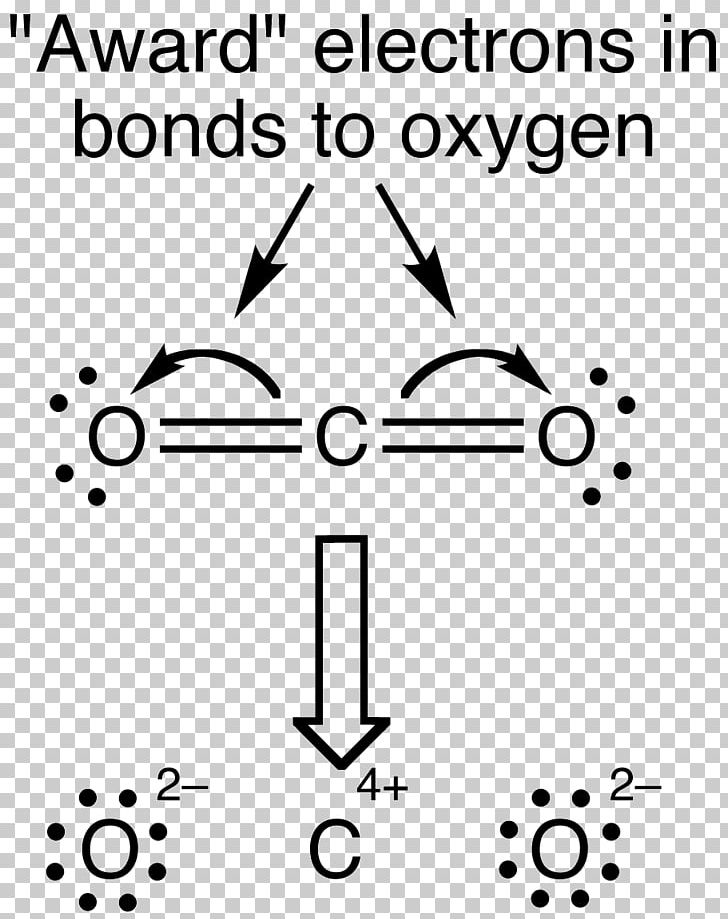
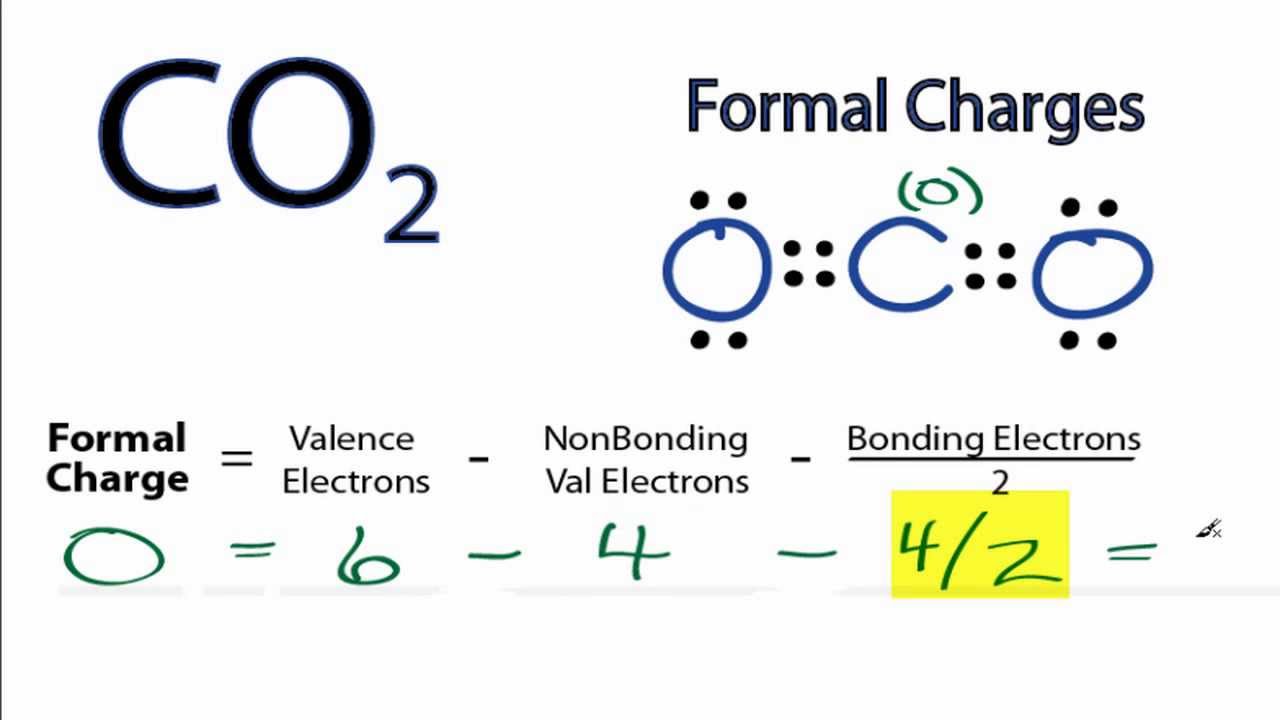
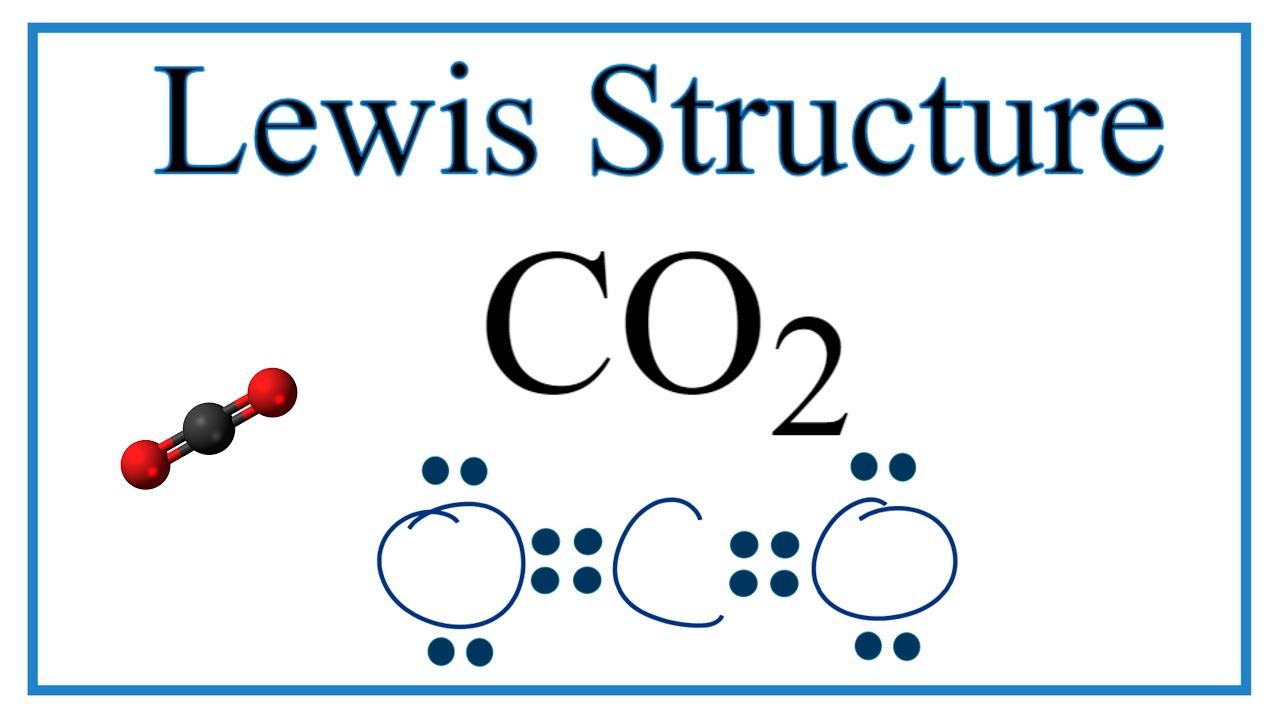
Formal Charge Carbon Dioxide Lewis Structure Chemical Bond Valence Electron PNG, Clipart, Angle, Atom, Black, Black

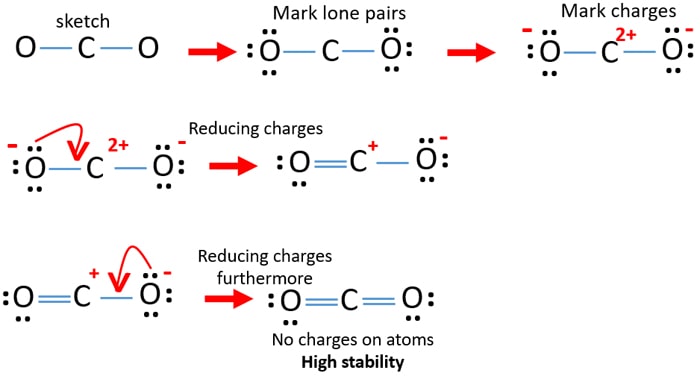
dipole - Is the carbon atom in the carbon dioxide molecule partially positive? - Chemistry Stack Exchange
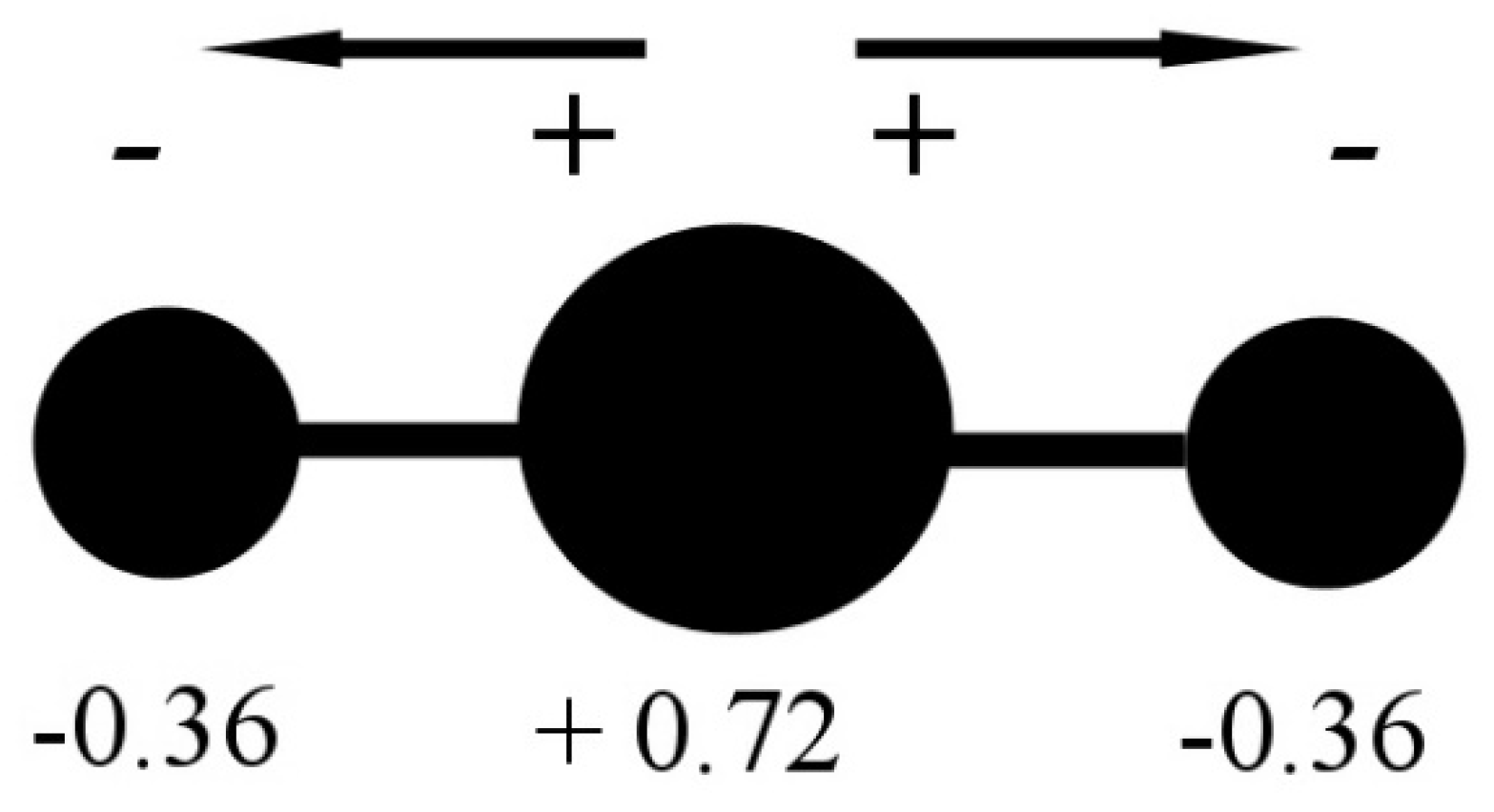
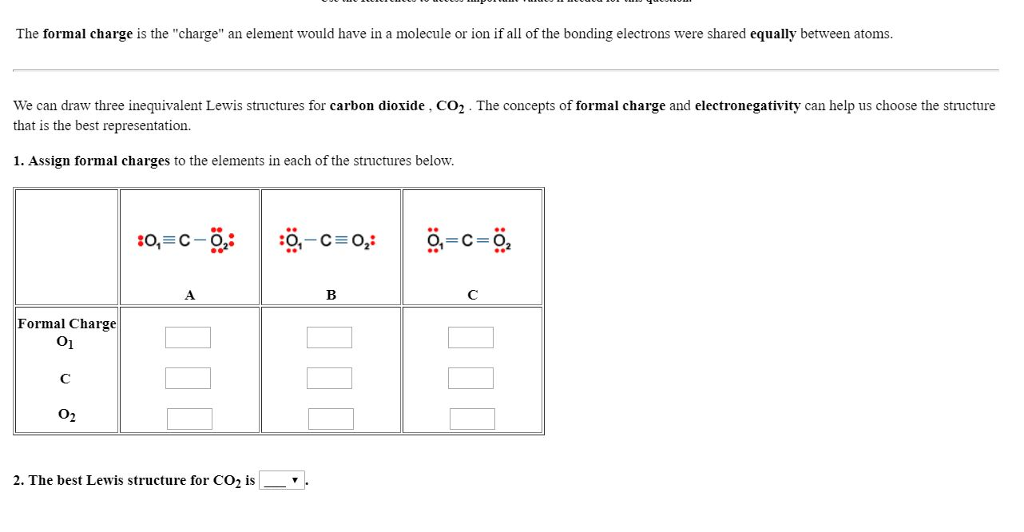
Minerals | Free Full-Text | CO2 Dipole Moment: A Simple Model and Its Implications for CO2-Rock Interactions

Why is carbon dioxide non-polar even though the C=O bonds are polar bonds but SO_2 is a polar compound? | Homework.Study.com